What Perform a Review of Current Research Means?
What is a Literature Review
A literature review is an objective, concise, critical summary of published enquiry literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article.
A literature review does Non:
A literature review does non simply reference and list all of the material you lot have cited in your newspaper.
- Presenting material that is non directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with "A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y" and merely listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good literature review DOES:
- Present a cursory typology that orders articles and books into groups to aid readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions well-nigh a enquiry topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your surface area of inquiry
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous enquiry indicates near a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the groundwork of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
Edifice Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to excogitate of a literature review is to call back nigh writing it as you would build a bookshelf. Yous don't demand to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, y'all can take the pieces that other researchers have cutting out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your ain "books"—that is, your own report methods, results, and conclusions.
What Makes a Expert Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the well-nigh of import elements that a literature review provides.
- A historical background for your inquiry: Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a pocket-sized way. Providing a historical background as well demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make certain to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your piece of work.
- The current context in which your enquiry is situated: Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, bug, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly beingness updated by new piece of work, you can testify where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
- A discussion of relevant theories and concepts that provide the foundation for your enquiry: For example, if y'all are researching the relationship between ecological environments and homo populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connexion to contextualize your study. If your report asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this management.
- A definition of the relevant terminology: In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. Just if you lot nowadays a term that is obscure or context-specific, yous should define the pregnant of the term in the Introduction section (if yous are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature beingness reviewed.
- A description of related enquiry that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work: You lot tin can apply your literature review as bear witness of what works, what doesn't, and what is missing in the field.
- Supporting evidence for a applied problem or event your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related enquiry establishes your expanse of inquiry as reputable and shows you are edifice upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews tin differ in structure, length, and amount and latitude of content included. They can range from the selective (a very narrow area of inquiry or only a unmarried work) to the comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They tin can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
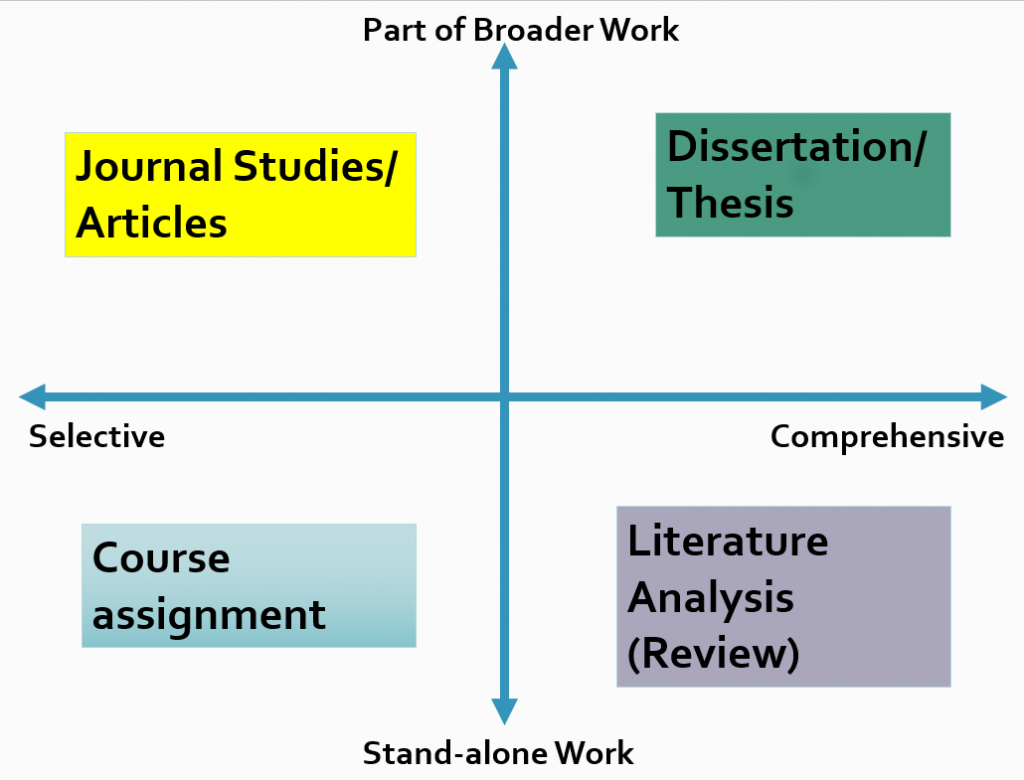
- A class assignment is an instance of a selective, stand up-solitary piece of work. It focuses on a pocket-size segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles commencement with a selective literature review to provide context for the inquiry reported in the study; such a literature review is unremarkably included in the Introduction section (just it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion department).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand equally a split work—in this case, the unabridged article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Type of Literature Reviews Found in Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly constitute in journals are those introducing inquiry articles (studies and surveys) and stand-solitary literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, unremarkably near the stop. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current report. Its purpose is to prepare research precedence and provide support for the report's theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles incorporate an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete department or indistinguishable from the balance of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the construction of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest groundwork information about a topic starting time and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale, finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often duplicate from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-lonely literature review
The literature review published every bit a stand-alone article presents and analyzes equally many of the of import publications in an expanse of written report as possible to provide background information and context for a current expanse of enquiry or a study. Stand up-lonely reviews are an splendid resource for researchers when they are start searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a scrap broader in scope and tin can extend further dorsum in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a "review article" refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors' own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that one time once more explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this assay is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms "Literature Review" or "Review of the Literature" in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or advisable tin can as well depend on the specific author instructions of the target periodical. Accept a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

Writing a Literature Review in 6 Steps
Then how do authors turn a network of manufactures into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not normally a linear process—authors ofttimes get dorsum and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their report. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the electric current work. This also means you will not exist writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it earlier, during, and subsequently your study is consummate.
Hither are some steps that volition help you brainstorm and follow through on your literature review.
Footstep 1: Choose a topic to write almost—focus on and explore this topic.
Cull a topic that yous are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers volition find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient inquiry conducted for a review. This will help you lot find the "sweet spot" for what to focus on.
Step 2: Enquiry and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations and theses—these and any other academic work related to your expanse of written report is called "the literature."
Step iii: Clarify the network of data that extends or responds to the major works in your expanse; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to place intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the fabric that will be nigh useful to y'all review.
Footstep iv: Describe and summarize each commodity—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your report.
Determine ii-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; accept notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to your topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given written report, perhaps some of the chief concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and so write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that innovate a study, these tin be relatively brusk. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more than texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this data might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond and/or confirm to those sections in your own report. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or bear witness a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are of import to include in your literature review. In improver, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings volition be valuable to review here.
Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5, but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the "golden thread" that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn't have before reading your literature review. Make sure y'all know where to put the research question, hypothesis, or argument of the trouble in your enquiry paper and so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions y'all want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your review will not but cover publications on your topics only will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps yous will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your enquiry and you tin plough a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.
In addition to these guidelines, authors also need to check which style guidelines to employ (APA, AMA, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might take for how to construction such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals' "Guide for Authors" pages.
Finally, after yous have finished drafting your literature review, exist sure to receive proofreading and language editing for your academic piece of work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by bookish journals will ensure that your paper is gear up for publication in your target journal.
Wordvice Resources
If you need more advice on how many references to include in your paper, how to write the abstract or title for your manuscript, or how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter, then head over to the Wordvice academic resource website.
Source: https://blog.wordvice.com/how-to-write-a-literature-review/
0 Response to "What Perform a Review of Current Research Means?"
Post a Comment